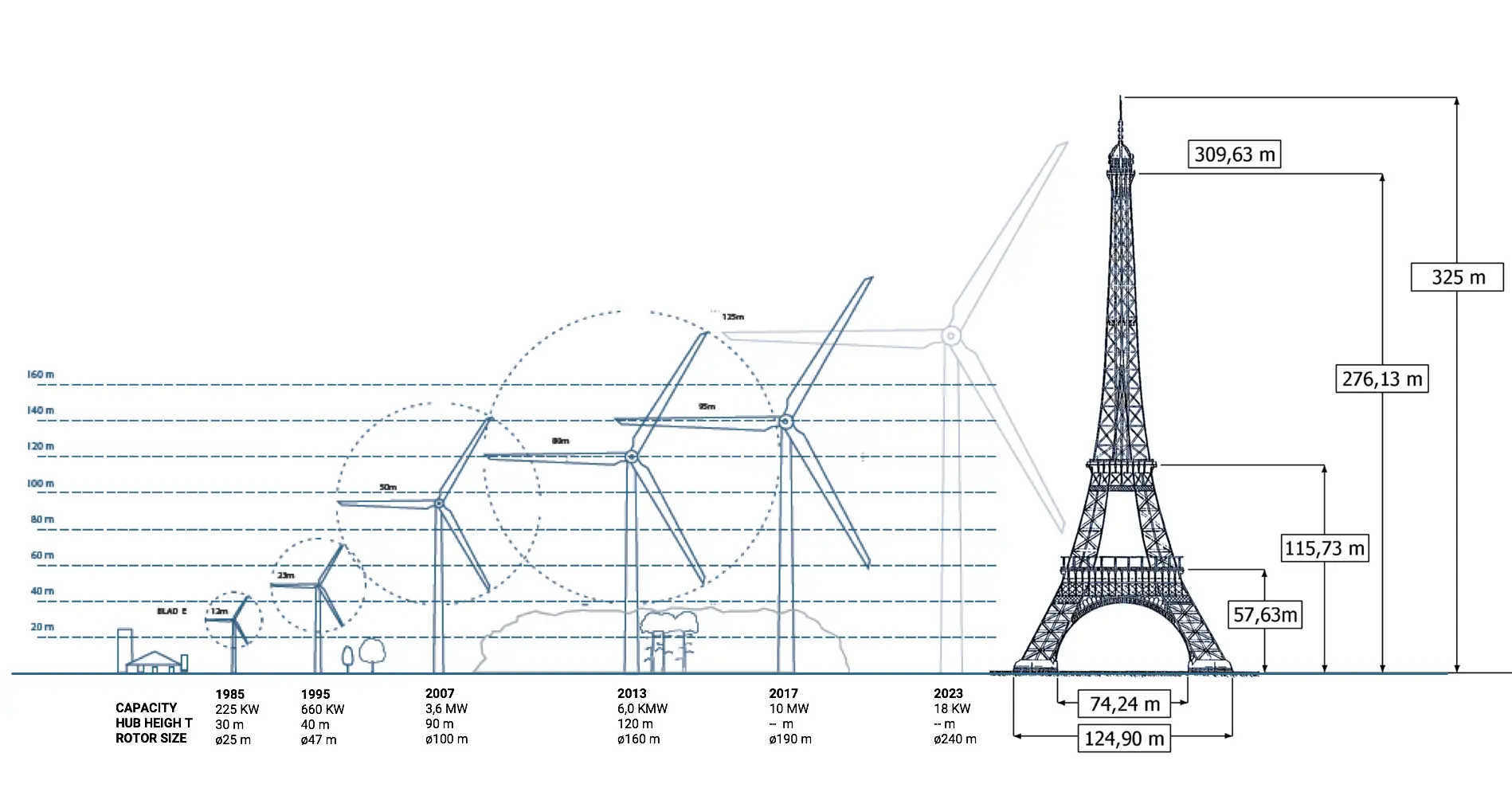
The growth rate of wind market
The installation of wind turbines in the world has had a high pace in recent years. According to statistics published by WWEA, the global wind turbine market reached a total capacity of 906 gigawatts in 2022 , enough to provide more than 9% of the world’s energy demand. Currently, 300,000 wind turbines are installed, which means that there is a fleet of one million blades that require supervision and maintenance care.
Wind turbine blades
Blades of a wind turbine are the largest one-piece composite structures built in the world, even larger than the wings of any aircraft. They undergo more than one billion load cycles during their operative life, thus making periodic inspection and maintenance essential to keep wind turbines in service.
Manned inspection methods have a limited ability to detect structural damage early, which is crucial to avoid extremely costly repairs, or to avoid catastrophic failures, and to be able to repair them in order to extend the life of a blade. With manned repair technologies it is possible to clean/sand and repair cracks situated on 1/3 of the blade, made by technicians accessing a confined space and unsanitary environment. It is not possible for the technicians to repair internally cracks in the other 2/3 of the blade, and these can spread further and could potentially generate a catastrophic failure. If cracks are detected before a structural failure, the blade would be discarded and replaced. In addition, the methods and technologies currently available for internal inspection and repair of the blades require long downtimes of the wind turbine, with the consequent economic loss for the operating company. They are jobs with a high cost, and involve exposing operators to work at height, in confined spaces and unsanitary environments.
How to detect internal blade damages
Technologies developed by WINDBOTIX are a game-changer in the scenario of internal repairs of wind blades. Our robot NEMO allows to inspect and detect internal cracks and structural damage along the structural beam at an early stage.
Below you can see real cases of inspection with a NEMO robot inside the beam, detecting structural cracks at different locations, as you can see:
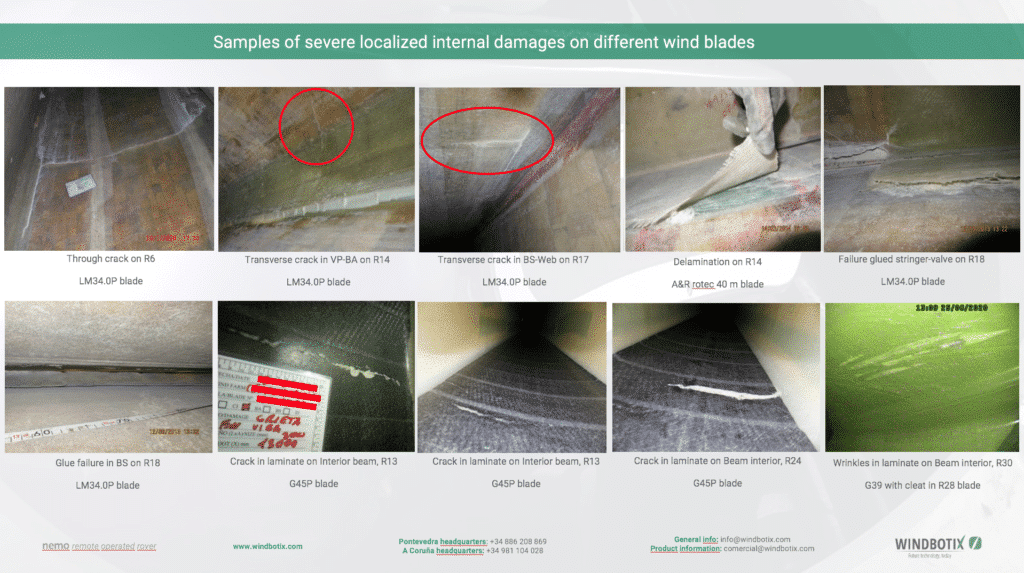
These types of cracks must be repaired as soon as possible, so as not to compromise the operation of the machine. The usual procedure is by removing layers by sanitizing by roughing/sanding, replacing layers by manual rolling and vacuum compaction and curing of laminate by heating blankets.
How to repair internal blade damages
Using robotic technologies we are able to make repetitive and reliable repair methods, capable to work in very small size, milling process, placing patch and curing process under controlled conditions.
Our patented robot CYRUS allows to repair internally blades along their critical areas, avoiding the access of operators to work inside confined space and harmful environment.
Several cases of real inspections and repairs have been analyzed, where the use of a repair robot would avoid discarding the blade, in addition to avoiding exposing technicians to harmful environments.
With conventional repair technologies it is only possible to clean and repair internally cracks up to Z15 m, but CYRUS allows to repair blade till Z30 m ( 75% of a LM43-8)